The Need for Prevention and Management
A Growing Health Crisis: The Prevalence of Neck Pain
According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, an estimated 203 million people grappled with neck pain in 2020. This number is expected to rise dramatically by 32.5%, translating to a total of 269 million affected individuals by 2050. The GBD study, which provides comprehensive data on the prevalence, impact, and burden of neck pain on individuals and healthcare systems worldwide, underscores the escalating health crisis posed by neck pain.
Neck Pain: A Significant Contributor to Global Disability
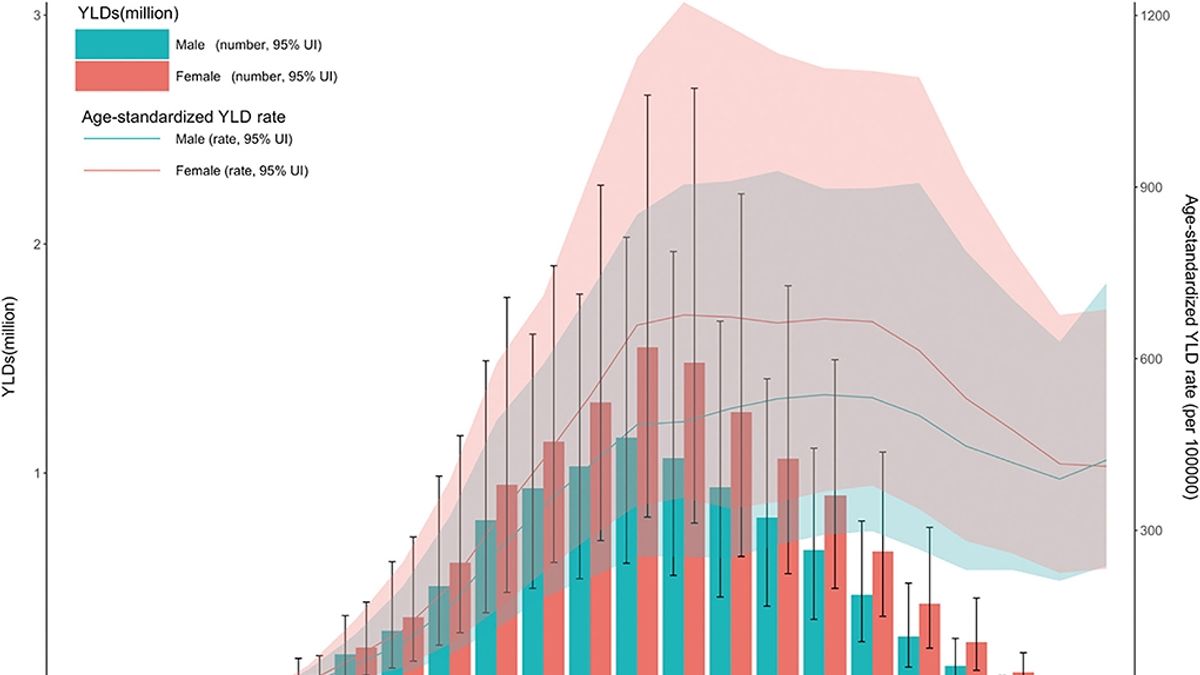
The GBD study goes further to rank neck pain as the fourth leading cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) worldwide. This statistic signifies the significant toll that neck pain takes on individuals’ quality of life and productivity. It also hints at the immense burden that neck pain places on healthcare systems globally, particularly in high-income countries where the prevalence is notably high.
Everyone is at Risk: The Ubiquitous Nature of Neck Pain
The study found that neck pain can affect people across all age brackets, making it a universal health concern. This widespread prevalence underscores the need for practical, scalable, and effective strategies to prevent and manage neck pain across diverse populations. It is crucial to understand that neck pain is not a selective disorder; it can impact anyone, anywhere, irrespective of their economic, demographic, or social background.
Implications for Healthcare Systems
The rise in neck pain cases presents significant challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. It demands a shift in focus towards preventive strategies to curb the growing prevalence. Effective management of neck pain can reduce the strain on healthcare resources, improve patient outcomes, and enhance overall population health. Therefore, addressing neck pain should be a top priority for health policymakers, practitioners, and researchers alike.
Prevention and Management of Neck Pain
Given the projected increase in neck pain cases, there is a critical need for effective prevention and management strategies. These may include public health initiatives to raise awareness about the risk factors for neck pain, ergonomic interventions to promote correct posture at work and home, and access to effective treatment options for those already suffering from the condition. Encouraging regular physical activity, promoting healthy lifestyles, and integrating neck pain management into primary healthcare services can also play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of this growing health concern.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The findings from the GBD study send a clear message: neck pain is a significant, growing health issue that demands immediate attention. The projected increase in the prevalence of neck pain presents a challenge that requires concerted efforts from individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers. By prioritizing prevention and management strategies, we can alleviate the burden of neck pain and improve the quality of life for millions of people worldwide. The time to act is now.
link